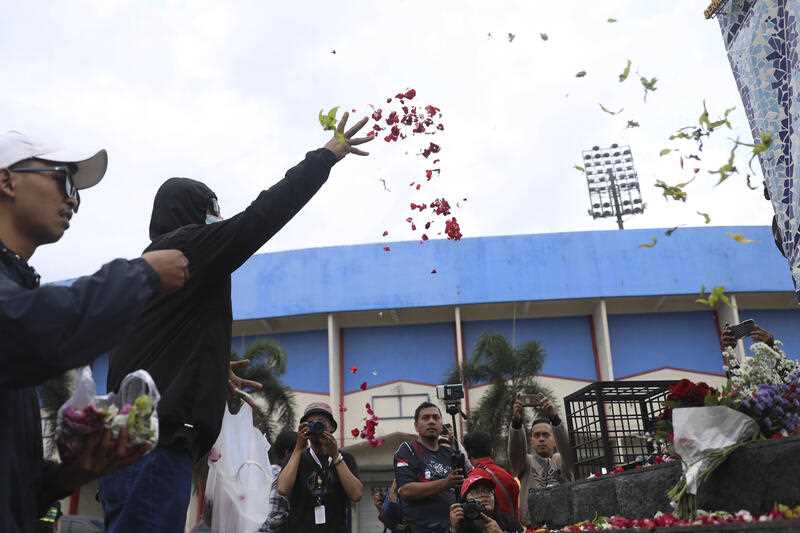Gaining the right to host next year’s Under-20 World Cup was a major milestone in Indonesia’s soccer development, raising hopes a successful tournament would turn around problems that had long blighted the sport in this country of 277 million people.
The death of at least 125 people at a league game between host Arema FC of East Java’s Malang city and Persebaya Surabaya on Saturday is a tragic reminder, however, that Indonesia is one of the most dangerous countries in which to attend a game.
“Do remember that the FIFA U-20 World Cup will be the worldwide spotlight since the event will be joined by 24 countries from five continents,” Indonesia’s President Joko Widodo said last month as he pushed for thorough preparations for the tournament.
Since Saturday, the domestic league has been suspended. Widodo has ordered the sports minister, the national police chief and the soccer federation to conduct a thorough investigation into the deadly stadium crush.
Indonesia was the first Asian team ever to play at a World Cup — participating in 1938 as Dutch East Indies — but despite a national passion for the sport, it has never returned after years of corruption, violence and mismanagement.
Data from Indonesia’s soccer watchdog, Save Our Soccer, showed 78 people have died in game-related incidents over the past 28 years.
Those accused are often associated with supporter groups that attach themselves to clubs, with the biggest boasting hundreds of thousands of members.
Arema’s intense rivalry with Surabaya meant no visiting fans were allowed in the stadium on the weekend. Yet violence broke out when the home team lost 3-2 and some of the 42,000 Arema fans, known as Aremania, threw bottles and other objects at players and soccer officials.
Restrictions on visiting fans also have failed in the past. In 2016, despite Persib Bandung supporters being banned from a game with bitter rival Persija Jakarta, they were blamed for the death of a Jakarta supporter.
A month earlier, a Persib fan had been beaten to death by Jakarta followers.
Soccer fans have accused security officials of being heavy-handed in the past and on the weekend, with witnesses describing officers beating them with sticks and shields before shooting tear gas canisters directly into the crowds.
“The police who were in charge of security violated FIFA stadium safety and security regulations,” soccer analyst Akmal Marhali told Indonesian media on Sunday, referring to the use of tear gas on Malang fans who entered the pitch after their team’s defeat. That sparked a rush for exits in an overcrowded stadium.
“The Indonesia Football Association may have been negligent for not informing the police that security procedures at a football match are not the same as those at a demonstration.”
FIFA prohibits the use of tear gas by on-field security or police at stadiums.
Indonesia’s soccer association, known locally as PSSI, has long struggled to manage the game domestically.
In 2007, Nurdin Halid was imprisoned on corruption charges but was able to continue as the organisation’s president until 2011. After Halid was banned from running for another term, a rival league, federation and national team emerged.
But chaotic administration continued until FIFA suspended Indonesia in 2015, a sanction lifted the following year.
In 2019, when FIFA awarded Indonesia hosting rights for the Under-20 World Cup, it was seen as a vote of confidence.
In June, a FIFA panel inspected the country’s soccer facilities and planning for the May 20-June 11 tournament and proclaimed its satisfaction.
FIFA has not yet commented on any potential impact on the Under-20 World Cup from the weekend tragedy, but it is likely to damage Indonesia’s bid to host the 2023 Asian Cup.
Get the latest news, sport, entertainment, lifestyle, competitions and more delivered straight to your inbox with the Canberra Daily Daily Newsletter. Sign up here.